AML Screening Agent
Updated on 12.09.25
1 minute to read
Copy link
Overview
SEON’s AML Screening Agent empowers AML teams to rapidly sift through customer screening matches by identifying false positives and highlighting discrepancies. This allows analysts to make faster, more informed decisions during the review process.
How it works
When reviewing a match result on the AML list page, you can enable the AML Screening Agent by selecting items with the checkbox in the bulk action navigation.
For example, you can filter for all reopened or new cases and then apply a bulk action review with the AML Screening Agent’s assistance.
In the list, you will see all results where the AML Screening Agent can provide you with additional insights.
Alternatively, you can start the AML Screening Agent directly from the AML Information widget’s result detail page.
On this page, you will find a button labeled Run AML Screening Agent, which allows you to launch the AML Screening Agent for the selected result.
Clicking this triggers the AI to evaluate the AML Customer Screening hits in real-time by:
- Cross-validating the hit with the input data
- Highlighting mismatches or weak associations
- Flagging likely false positives for your review
If no false positives are identified, the system will show the following message:
- No false positives have been found.
Key features
Hit summary
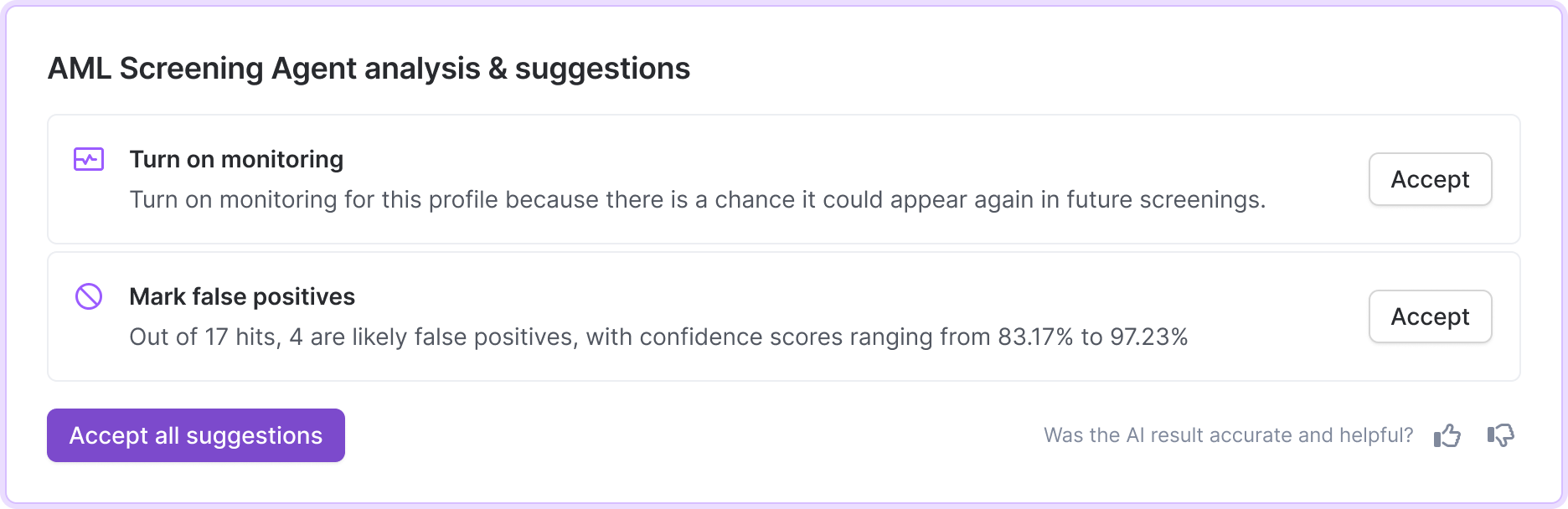
At the top of the page, you'll see a summary of how many hits AI marked as likely false positives. You can optionally bulk accept these suggestions.
Visual indicators
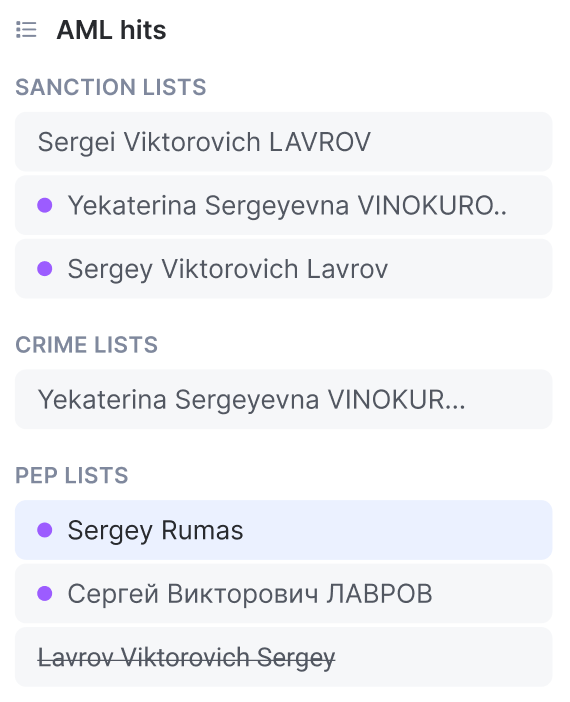
On the left sidebar, purple dots appear next to hits flagged by AI as false positives.
Explanations with confidence score
Each flagged hit includes a short explanation of the discrepancy, along with a confidence score (%) that shows how confident the AI is that the hit is a false positive.

How it helps
AML Customer Screening typically uses fuzzy matching to comply with global regulatory expectations. This helps ensure that potential bad actors are not missed due to small name variations (e.g., transliteration, middle initials or omitted middle names).
However, fuzzy matching also introduces noise — creating numerous false positives that slow down analysts.
AI solves this by flagging irrelevant matches and pinpointing genuine discrepancies within milliseconds, letting analysts remain in control of the final decision.
How to run the AML Screening Agent
1. Open a new or re-opened hit in your AML queue.
2. On the Result detail page, click Run AML Screening Agent.
3. Review the results:
- Check for purple dots indicating false positives.
- Read the explanation and confidence score for each flagged item.
4. If you agree with the AI's suggestion:
- Mark the result as a false positive.
- Update the hit status to Reviewed.
What kind of false positives can AI flag?
Below is a categorized list of the most common discrepancies the AI is trained to detect.
Company name mismatches
- Different company types: The business designators don’t match (e.g., Ltd vs GmbH), which could indicate different legal entities.
- Company name doesn’t match: The submitted company name is significantly different from the one in the result.
- AKA company type doesn’t match: Alternate names (AKAs) use different company types or formats.
- AKA company name doesn’t match: The alternate names (AKAs) of the company do not align.
- Wrong company jurisdiction: The legal form of the company is used in a different country or legal system, suggesting a mismatch.
Country mismatches
- Different country: The country in the search input and the result do not match.
Date of birth (DOB) issues
- Different birth date: The DOB in the result is different from the one searched.
- Year of birth doesn’t match: The birth year is different between your search and the result.
Sanctions expirations
- Sanction status may be outdated: The result shows old sanctions data that may no longer apply.
- No longer active (terminated): The entity appears to have been terminated or no longer exists.
Name mismatches
- Different first name: The first names in the result and the input differ.
- Different last name: The last names don’t match.
- Spelling or formatting difference: There may be a spelling difference or formatting issue (e.g., middle names/initials).
PEPs discrepancies
- Too young to be a PEP: The person’s age doesn’t align with holding a political position, indicating a likely mismatch.
- Political role is outdated: The individual may no longer hold the political position (PEP).
Adverse media
In your Adverse Media results, the AI Agent helps you identify expired or outdated articles.